IBD Research and Clinical Trials
Crohn's disease is a common condition of the intestines (bowels) that affects approximately 1.5 million people in the United States. Crohn's usually affects young adults (patients in their 20s and 30s),but can affect children and older adults as well. The cause of Crohn's disease is not known; however, most experts agree that genetics (traits passed on from your parents), the environment, and the patient's immune system (cells that fight off infection) play an important role in the disease.
Crohn's disease can affect any part of the digestive tract: mouth, esophagus, stomach, duodenum, jejunum, ileum, colon, and anus. The most common area affected is the part of the small bowel called the ileum. The inflammation usually occurs in segments, with healthy segments of bowel in between inflamed segments. It is called Crohn's ileitis when only the ileum is affected. It is called Crohn's colitis when only the colon is affected. And it is called Crohn's ileocolitis when both the ileum and the colon are affected.
Unfortunately, there is no cure for Crohn's disease and patients must deal with the illness for their entire lifetime. Patients typically will have periods of active symptoms ("flares") followed by symptom-free periods ("remission"). The symptoms can have a negative impact on quality of life for patients. However, most patients continue to work and have productive lives.
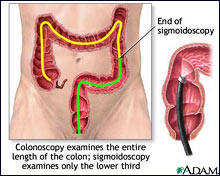
Many different tests are used to diagnosis patients with Crohn's disease. Patients are given a complete history and physical exam. Tests that may be given include blood tests, stool tests, CT or MRI scans, and colonoscopy with biopsy. The colonoscopy will look for ulcers or inflammation in the intestine.
There is no cure for Crohn's Disease at this time, although this is an important area of current research. Treatment helps to eliminate or reduce symptoms, prevent flares, and decrease complications of the disease.
Current therapies to treat patients with Crohn's disease include aminosalicylates ("5-ASA"), steroids, immune suppressants, and biologic therapy (medications that block specific inflammatory molecules important in Crohn's disease). For some of these drugs, treatments are available in pill form, enemas, injections under the skin, and intravenous infusions. Although medical treatment can be effective in controlling the symptoms of Crohn's disease, patients must take medications continuously to prevent the symptoms from returning.
Surgery to remove the part of the intestine that is inflamed is an important part of IBD therapy. Although surgery usually relieves symptoms of Crohn's disease, it does not offer a cure. One-third of patients require repeat operations without medical therapy. There have been many advances in surgery for Crohn's disease. One is the use of bowel-saving techniques such as stricturoplasty (repair of disease segments instead of removal) and minimally invasive surgery (laparoscopy).
Smoking worsens the symptoms in patients with Crohn's disease. If you stop smoking, the inflammation in your intestines may decrease and your symptoms may go away.
Changing your diet, especially during flares, may ease your symptoms. It will not reduce inflammation, nor will it lower your risk for complications. However, dietary changes may make you feel better.
Herbal, alternative, or complementary therapies have not been proven to work in clinical studies, nor have they been fully tested. Although some help ease symptoms, they usually work only in very mild cases or as a supplement to existing therapy. Ask your health care team about the safety and effects of these products. Always let your health care team know if you are using them.
