Cardiac Calcium Scoring (Heart Scan)
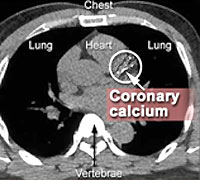
The coronary arteries are the vessels that supply oxygen-rich blood to the heart. Plaque — made of fat, calcium and other substances — can build up and narrow or close the arteries.
To detect this build-up, your physician may order cardiac calcium scoring — a test that is also known as coronary artery calcium (CAC) scoring, a heart scan or calcium score.
The procedure is performed at the University Imaging Center at UMMC. To make an appointment call 410-328-3225.
This non-invasive CT scan (computed tomography) of the heart calculates your risk of developing coronary artery disease (CAD) by measuring the amount of calcified plaque in the coronary arteries.
Plaque or calcium build-up in the coronary arteries causes heart disease or can lead to a heart attack. The coronary calcium scan is a better predictor of coronary events than cholesterol screening or other risk factor assessments.
About Your CAC Score
A calcium score (sometimes called an Agatston score) is calculated based on the amount of plaque observed in the CT scan. It may be converted to a percentile rank based on your age and gender. The results from your cardiac scoring will be sent to your doctor.
Your likelihood of having heart disease or a heart attack correlates with your calcium scoring. The lower your calcium score and percentile rank, the less likely you are to have a cardiac event compared to other men or women your age.
Calcium Score Results
The purpose of the test is to understand your risk of heart attack or disease, taking preventive or corrective measures based on the results.
If you have any plaque present (a score greater than 0), your doctor may make recommendations for lifestyle changes, such as quitting smoking, eating better and exercising more. The higher your score the more treatment your doctor may recommend.
If you have a high score, you can make an appointment with one of our coronary artery disease specialists.
Zero: No plaque. Your risk of heart attack is low.
1 - 10: Small amount of plaque. You have less than a 10 percent chance of having heart disease, and your risk of heart attack is low.
11-100: Some plaque. You have mild heart disease and a moderate chance of heart attack. Your doctor may recommend other treatment in addition to lifestyle changes.
101 - 400: Moderate amount of plaque. You have heart disease and plaque may be blocking an artery. Your chance of having a heart attack is moderate to high. Your health professional may want more tests and may start treatment.
Over 400: Large amount of plaque. You have more than a 90 percent chance that plaque is blocking one of your arteries. Your chance of heart attack is high. Your health professional will want more tests and will start treatment.
Getting a Calcium Score Test
At UMMC, because this test emits a low dose of radiation, a written referral from your doctor is required. It can be faxed ahead of time to our office at 410-328-0124 or can be brought with you at the time of service.
What Happens During a CT Heart Scan
The procedure is performed by a CT technologist with the assistance of a radiologist.
Once you arrive, you may have to change into a gown if there is any metal on your clothing. The technologist will explain the procedure to you and escort you to the CT room.
You will lie on your back on the CT table and EKG electrodes will be placed on your chest to monitor your heart rate. The CT table will move in very small increments every few seconds and take pictures.
You may be asked to hold your breath for 20 to 30 seconds, and you will need to hold perfectly still. Even though you will be left alone in the room, the technologist will watch you through a window, and you will be able to speak to him or her.
The scan takes approximately 20-30 seconds, but from start to finish it takes approximately 10-15 minutes.
To schedule an appointment, please contact the Radiology Access Center at 410-328-3225.
